Your Superior mesenteric vein thrombosis management images are available in this site. Superior mesenteric vein thrombosis management are a topic that is being searched for and liked by netizens today. You can Get the Superior mesenteric vein thrombosis management files here. Download all free vectors.
If you’re searching for superior mesenteric vein thrombosis management pictures information connected with to the superior mesenteric vein thrombosis management interest, you have pay a visit to the ideal site. Our site frequently provides you with hints for viewing the maximum quality video and image content, please kindly hunt and locate more enlightening video articles and graphics that fit your interests.
Superior Mesenteric Vein Thrombosis Management. Transcatheter therapeutic techniques in management of symptomatic portal and mesenteric venous thrombosis. 1 2 Extension to mesenteric venous arches causes intestinal infarction with a reported mortality of up to 50. Online ahead of print. Idiopathic Superior Mesenteric Vein Thrombosis Resulting in Small Bowel Ischemia in a Pregnant Woman articleLin2011IdiopathicSM titleIdiopathic Superior Mesenteric Vein Thrombosis Resulting in Small Bowel Ischemia in a Pregnant Woman authorHao Lin and Chih-Che Lin and Wanting.
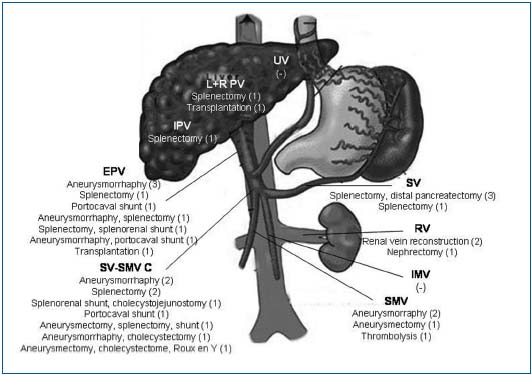 Current Management Of Visceral Venous Aneurysms Servier Phlebolymphologyservier Phlebolymphology From phlebolymphology.org
Current Management Of Visceral Venous Aneurysms Servier Phlebolymphologyservier Phlebolymphology From phlebolymphology.org
Combining endovascular therapy with open surgery hybrid approach has been described in a modern series of nine patients 15 where bowel resection was followed by fluoroscopic-guided balloon thrombectomy after surgical exposure of the superior mesenteric vein ending up with completion control venography. Patient was managed by resection of the necrotic bowel venous decompression by venous bypass from superior mesenteric vein to the right ovarian vein and open abdomen with negative pressure wound therapy NPWT. Mesenteric venous thrombosis usually involves the superior mesenteric vein with the danger of bowel infarction. Immediate systemic anticoagulation and early surgical intervention are required to remove the infracted segment of bowel to prevent sepsis and death. J Pharm Pract. Online ahead of print.
Acosta 12 and S.
This is often employed for patients who present with signs of peritoneal irritation. Mesenteric vein thrombosis almost always involves the distal small intestine superior mesenteric venous drainage and rarely involves the colon inferior mesenteric venous drainage. The newer imaging techniques allow earlier diagnosis. Combining endovascular therapy with open surgery hybrid approach has been described in a modern series of nine patients 15 where bowel resection was followed by fluoroscopic-guided balloon thrombectomy after surgical exposure of the superior mesenteric vein ending up with completion control venography. This is a case report of a 55-year-old Caucasian male prescribed topical testosterone therapy for 12 months prior to admission when he was diagnosed with acute thrombosis in the portal vein PVT and. Mesenteric venous thrombosis usually involves the superior mesenteric vein with the danger of bowel infarction.
 Source: thelancet.com
Source: thelancet.com
Treatment of superior mesenteric and portal vein thrombosis with direct thrombolytic infusion via an operatively placed mesenteric catheter Kaplan JLWeintraub SLHunt JPGonzalez ALopera JBrazzini A The American surgeon 2004 Jul PubMed PMID. This article analyses the treatment options for acute PVTMVT. Patient was managed by resection of the necrotic bowel venous decompression by venous bypass from superior mesenteric vein to the right ovarian vein and open abdomen with negative pressure wound therapy NPWT. Acute mesenteric venous thrombosis accounts for up to 20 of all patients with acute mesenteric ischemia in high-income countries. Several cases of vascular thrombosis with pulmonary embolism and mesenteric and portal vein thrombosis have been documented Most of these findings have been reported in critically ill patients with elevated acute phase reactants and deranged coagulation.
 Source: slideplayer.com
Source: slideplayer.com
When you have mesenteric venous thrombosis MVT you have a blood clot in a vein around where your intestines attach to your belly. Patient was managed by resection of the necrotic bowel venous decompression by venous bypass from superior mesenteric vein to the right ovarian vein and open abdomen with negative pressure wound therapy NPWT. The management of mesenteric vein thrombosis. When you have mesenteric venous thrombosis MVT you have a blood clot in a vein around where your intestines attach to your belly. Clinically separate from portal venous thrombosis due to a higher proportion of associated thrombophilic disorders and intestinal infarction SMV thrombosis warrants a distinct approach to management.
 Source: researchgate.net
Source: researchgate.net
Initially the clinical management should identify patients with an intra-abdominal focus requiring immediate surgical intervention eg. Several cases of vascular thrombosis with pulmonary embolism and mesenteric and portal vein thrombosis have been documented Most of these findings have been reported in critically ill patients with elevated acute phase reactants and deranged coagulation. Acute mesenteric venous thrombosis accounts for up to 20 of all patients with acute mesenteric ischemia in high-income countries. Initially the clinical management should identify patients with an intra-abdominal focus requiring immediate surgical intervention eg. J Pharm Pract.
 Source: researchgate.net
Source: researchgate.net
This article analyses the treatment options for acute PVTMVT. J Pharm Pract. 3 4 Without recanalization a cavernoma develops associated with a permanent risk of potentially fatal. SMV superior mesenteric vein 3D three-dimensional Index terms. Patient was managed by resection of the necrotic bowel venous decompression by venous bypass from superior mesenteric vein to the right ovarian vein and open abdomen with negative pressure wound therapy NPWT.
 Source: mayoclinicproceedings.org
Source: mayoclinicproceedings.org
Portal-mesenteric vein thrombosis pylephlebitis and liver abscesses are rare complications of inflammatory bowel disease IBD. The purpose of this case report is to relate an unusual presentation of CD in order to show how conservative treatment could be an appropriate option as a bridge to the surgery in patients with septic thrombophlebitis and multiple liver. Acute superior mesenteric vein thrombosis results in sudden interruption of blood supply to a segment of small intestine leading to ischemia followed by intestinal infarction and necrosis of that segment. Another possibility is thrombolysis either administered systemically or locally. 3 4 Without recanalization a cavernoma develops associated with a permanent risk of potentially fatal.
 Source: mayoclinicproceedings.org
Source: mayoclinicproceedings.org
Patient was managed by resection of the necrotic bowel venous decompression by venous bypass from superior mesenteric vein to the right ovarian vein and open abdomen with negative pressure wound therapy NPWT. Acosta 12 and S. Portal-mesenteric vein thrombosis pylephlebitis and liver abscesses are rare complications of inflammatory bowel disease IBD. This article analyses the treatment options for acute PVTMVT. 3 4 Without recanalization a cavernoma develops associated with a permanent risk of potentially fatal.
 Source: slidetodoc.com
Source: slidetodoc.com
Computed tomography CT angiography 95712916 95912916 Magnetic resonance MR vascular studies 95712942. Several cases of vascular thrombosis with pulmonary embolism and mesenteric and portal vein thrombosis have been documented Most of these findings have been reported in critically ill patients with elevated acute phase reactants and deranged coagulation. The newer imaging techniques allow earlier diagnosis. Two cases of superior mesenteric vein thrombosis were reported in which the patients had pre-existing lupus anticoagulant present in their blood samples 89. This article analyses the treatment options for acute PVTMVT.
 Source: sciencedirect.com
Source: sciencedirect.com
Portal-mesenteric vein thrombosis pylephlebitis and liver abscesses are rare complications of inflammatory bowel disease IBD. Acosta 12 and S. A single institutions experience. Initially the clinical management should identify patients with an intra-abdominal focus requiring immediate surgical intervention eg. Clinically separate from portal venous thrombosis due to a higher proportion of associated thrombophilic disorders and intestinal infarction SMV thrombosis warrants a distinct approach to management.
 Source: researchgate.net
Source: researchgate.net
Acosta 12 and S. When you have mesenteric venous thrombosis MVT you have a blood clot in a vein around where your intestines attach to your belly. The present case report describes the unusual progression of COVID-19 disease from pneumonia to a procoagulant state leading to superior mesenteric artery thrombosis and subsequent gut. Operative interventions include thrombectomy with thrombolysis. Online ahead of print.
 Source: researchgate.net
Source: researchgate.net
Acosta 12 and S. Several cases of vascular thrombosis with pulmonary embolism and mesenteric and portal vein thrombosis have been documented Most of these findings have been reported in critically ill patients with elevated acute phase reactants and deranged coagulation. The present case report describes the unusual progression of COVID-19 disease from pneumonia to a procoagulant state leading to superior mesenteric artery thrombosis and subsequent gut. Subsequently emphasis is placed on the recanalization of the PVMV or at least the prevention of thrombus extension to avoid long. Acute mesenteric venous thrombosis is nowadays.
 Source: semanticscholar.org
Source: semanticscholar.org
It is important to mention that our patient had the formation of a massive thrombosis in the SMV which had extended to the portal vein. Mesenteric venous thrombosis usually involves the superior mesenteric vein with the danger of bowel infarction. 1 2 Extension to mesenteric venous arches causes intestinal infarction with a reported mortality of up to 50. This is often employed for patients who present with signs of peritoneal irritation. The purpose of this case report is to relate an unusual presentation of CD in order to show how conservative treatment could be an appropriate option as a bridge to the surgery in patients with septic thrombophlebitis and multiple liver.

Acosta 12 and S. Acute portal vein thrombosis PVT is characterized by the recent development of a thrombus in the portal vein or its left or right branches. COVID-19 infection is associated with a hypercoagulable state similar to various cytokine release syndromes. Management of mesenteric and portal vein thrombosis includes both operative and nonoperative approaches. The present case report describes the unusual progression of COVID-19 disease from pneumonia to a procoagulant state leading to superior mesenteric artery thrombosis and subsequent gut.
 Source: researchgate.net
Source: researchgate.net
Transcatheter therapeutic techniques in management of symptomatic portal and mesenteric venous thrombosis. Operative interventions include thrombectomy with thrombolysis. Clinically separate from portal venous thrombosis due to a higher proportion of associated thrombophilic disorders and intestinal infarction SMV thrombosis warrants a distinct approach to management. 1 2 Extension to mesenteric venous arches causes intestinal infarction with a reported mortality of up to 50. Mesenteric vein thrombosis almost always involves the distal small intestine superior mesenteric venous drainage and rarely involves the colon inferior mesenteric venous drainage.
 Source: researchgate.net
Source: researchgate.net
J Pharm Pract. A systematic review of contemporary studies S. SMV superior mesenteric vein 3D three-dimensional Index terms. Computed tomography CT angiography 95712916 95912916 Magnetic resonance MR vascular studies 95712942. Idiopathic Superior Mesenteric Vein Thrombosis Resulting in Small Bowel Ischemia in a Pregnant Woman articleLin2011IdiopathicSM titleIdiopathic Superior Mesenteric Vein Thrombosis Resulting in Small Bowel Ischemia in a Pregnant Woman authorHao Lin and Chih-Che Lin and Wanting.
 Source: thoracickey.com
Source: thoracickey.com
Management of acute mesenteric venous thrombosis. The management of mesenteric vein thrombosis. Combining endovascular therapy with open surgery hybrid approach has been described in a modern series of nine patients 15 where bowel resection was followed by fluoroscopic-guided balloon thrombectomy after surgical exposure of the superior mesenteric vein ending up with completion control venography. This article analyses the treatment options for acute PVTMVT. When you have mesenteric venous thrombosis MVT you have a blood clot in a vein around where your intestines attach to your belly.
 Source: sciencedirect.com
Source: sciencedirect.com
Another possibility is thrombolysis either administered systemically or locally. Clinically separate from portal venous thrombosis due to a higher proportion of associated thrombophilic disorders and intestinal infarction SMV thrombosis warrants a distinct approach to management. Acute portal vein thrombosis PVT is characterized by the recent development of a thrombus in the portal vein or its left or right branches. Idiopathic Superior Mesenteric Vein Thrombosis Resulting in Small Bowel Ischemia in a Pregnant Woman articleLin2011IdiopathicSM titleIdiopathic Superior Mesenteric Vein Thrombosis Resulting in Small Bowel Ischemia in a Pregnant Woman authorHao Lin and Chih-Che Lin and Wanting. Initially the clinical management should identify patients with an intra-abdominal focus requiring immediate surgical intervention eg.
 Source: thegastroenterologist.ro
Source: thegastroenterologist.ro
Acute mesenteric venous thrombosis is nowadays. Nonoperative approaches can be either noninvasive or invasive. Authors present a case of a patient after pancreatoduodenectomy complicated by the thrombosis of superior mesenteric vein. Acute portal vein thrombosis PVT is characterized by the recent development of a thrombus in the portal vein or its left or right branches. Computed tomography CT angiography 95712916 95912916 Magnetic resonance MR vascular studies 95712942.
 Source: researchgate.net
Source: researchgate.net
Acute mesenteric venous thrombosis is nowadays. Online ahead of print. Initial treatment goal is cessation of thrombotisation and enabling of bodys fibrinolytic activity for destruction of the thrombus. Management of mesenteric and portal vein thrombosis includes both operative and nonoperative approaches. Administration of the therapeutic dosage of heparin provides immediate effect.
This site is an open community for users to do sharing their favorite wallpapers on the internet, all images or pictures in this website are for personal wallpaper use only, it is stricly prohibited to use this wallpaper for commercial purposes, if you are the author and find this image is shared without your permission, please kindly raise a DMCA report to Us.
If you find this site serviceableness, please support us by sharing this posts to your own social media accounts like Facebook, Instagram and so on or you can also save this blog page with the title superior mesenteric vein thrombosis management by using Ctrl + D for devices a laptop with a Windows operating system or Command + D for laptops with an Apple operating system. If you use a smartphone, you can also use the drawer menu of the browser you are using. Whether it’s a Windows, Mac, iOS or Android operating system, you will still be able to bookmark this website.