Your Chronic superior mesenteric vein thrombosis radiology images are available. Chronic superior mesenteric vein thrombosis radiology are a topic that is being searched for and liked by netizens now. You can Get the Chronic superior mesenteric vein thrombosis radiology files here. Download all royalty-free photos and vectors.
If you’re searching for chronic superior mesenteric vein thrombosis radiology pictures information connected with to the chronic superior mesenteric vein thrombosis radiology topic, you have come to the right site. Our site always provides you with hints for seeing the maximum quality video and picture content, please kindly hunt and locate more informative video articles and images that match your interests.
Chronic Superior Mesenteric Vein Thrombosis Radiology. In one retrospective study on 60 patients with chronic thrombosis of PVs or superior mesenteric veins 39 with variceal bleeding 18 with thrombophilia 9 with variceal bleeding received anticoagulation with recanalization of veins in 3 patients whereas none of the patients who were not anticoagulated recanalized the veins. A Contrast-enhanced maximum intensity projection magnetic resonance MR angiogram reveals collateral vessels from a superior mesenteric vein branch via submucosal varices into liver. Its branches are patent. MVT accounts for 1 in 5000 to 15000 inpa - tient admissions and 1 in 1000 emer-.
 Superior Mesenteric Venous Thrombosis Radiology Reference Article Radiopaedia Org From radiopaedia.org
Superior Mesenteric Venous Thrombosis Radiology Reference Article Radiopaedia Org From radiopaedia.org
Patients with recovery compared with patients with chronic mesenteric venous thrombosis showed more frequent central lesions p 003. 10 Further recurrent bleeding was. Mesenteric ischemia is a disease seen predominantly in the elderly that can be associated with considerable mortality if not detected before bowel infarction. Chronic mesenteric venous thrombosis is differentiated from acute mesenteric venous thrombosis by the existence of collateral venous circulation and cavernoma around the thrombosed vein. VLS enables objective and quantitative determination of GI mucosal ischemia. Furthermore bowel ischemia may not develop immediately.
VLS enables objective and quantitative determination of GI mucosal ischemia.
The anatomic site of involvement in acute mesenteric venous thrombosis is most often ileum 64 to 83 percent or jejunum 50 to 81 percent followed by colon. The symptoms are usually not typical enough to offer a clinical diagnosis. Acute portal vein thrombosis PVT is characterized by the recent development of a thrombus in the portal vein or its left or right branches. 2 The modality provides. Venous causes of acute mesenteric ischemia are less common 515 of cases 49 and are most often the result of a thrombosis of the superior mesenteric vein SMV. Reversible superior mesenteric vein thrombosis in acute pancreatitis.
 Source: radiopaedia.org
Source: radiopaedia.org
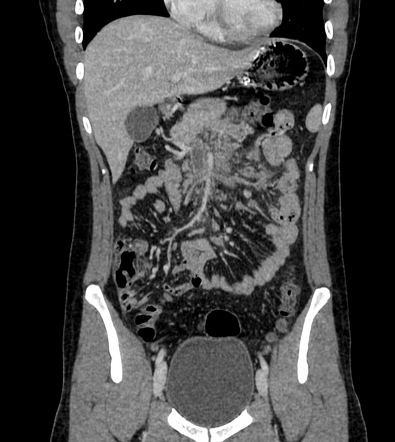
At diagnosis the thrombosed segment was shorter and. Main portal vein is dilated 145mm. At diagnosis the thrombosed segment was shorter and. Chronic mesenteric venous thrombosis accounts for approximately 20 to 40 of total mesenteric venous thrombosis cases and rarely causes intestinal infarction. The portal vein is formed by the confluence of the splenic and superior mesenteric veins which drain the spleen and small intestine respectively Occlusion of the portal vein by thrombus portal vein thrombosis PVT typically occurs in patients with cirrhosis andor prothrombotic disorders Chronic PVT develops in patients with acute PVT.
 Source: radiopaedia.org
Source: radiopaedia.org
Further investigation ruled out haematological causes and COVID-19 was. 10 Further recurrent bleeding was. A 68-year-old man was referred to the general surgeons on account of his abdominal pain of unknown cause. The diagnosis of mesenteric vein thrombosis relies heavily on imaging. Main portal vein is dilated 145mm.
 Source: radiopaedia.org
Source: radiopaedia.org
MVT accounts for 1 in 5000 to 15000 inpa - tient admissions and 1 in 1000 emer-. Reversible superior mesenteric vein thrombosis in acute pancreatitis. Main portal vein is dilated 145mm. Mesenteric venous thrombosis MVT describes acute subacute or chronic thrombosis of the superior or inferior mesenteric vein or branches. 1 2 Extension to mesenteric venous arches causes intestinal infarction with a reported mortality of up to 50.
 Source: radiopaedia.org
Source: radiopaedia.org
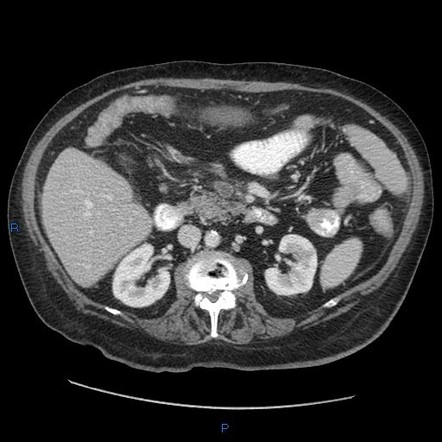
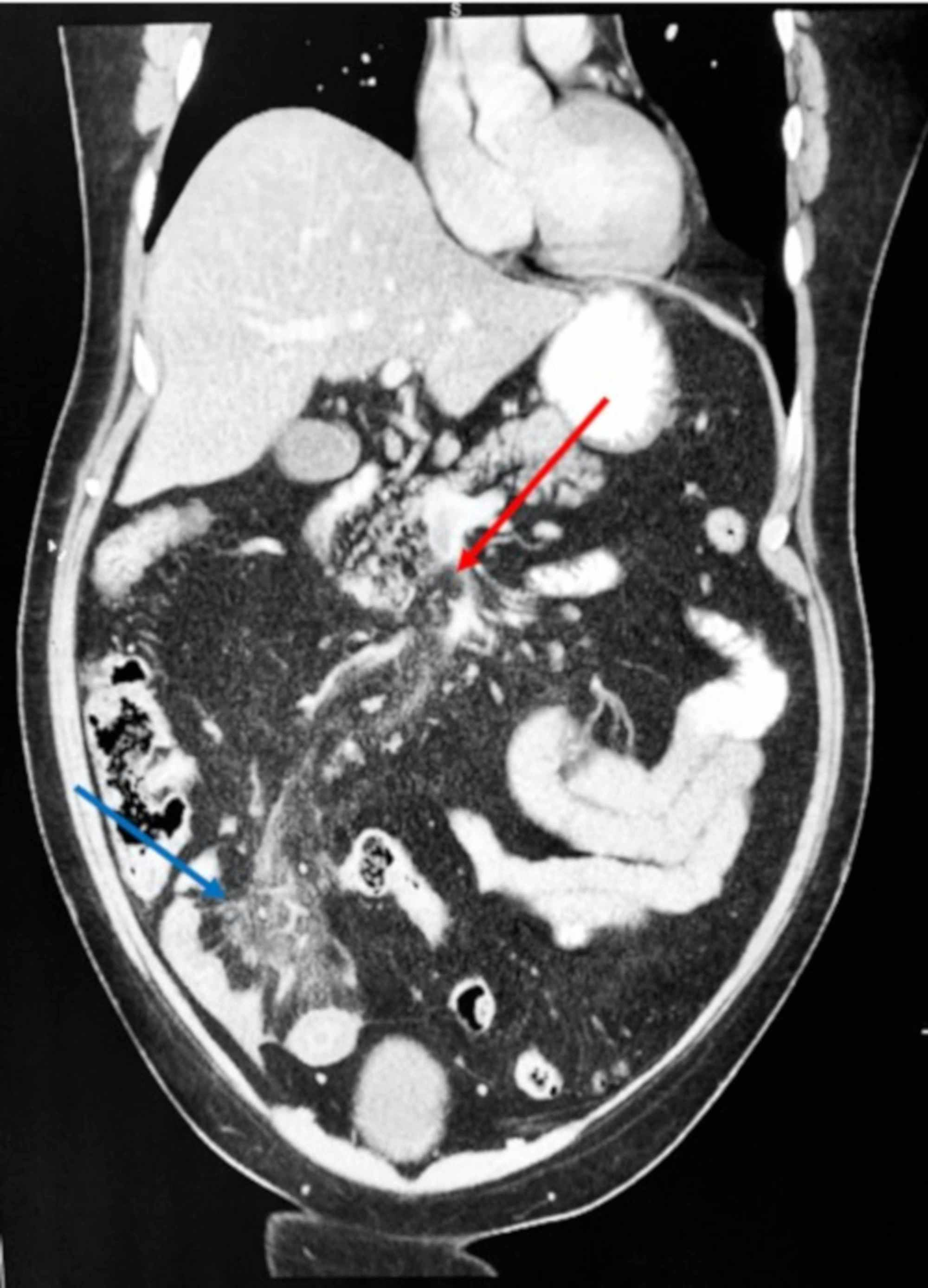
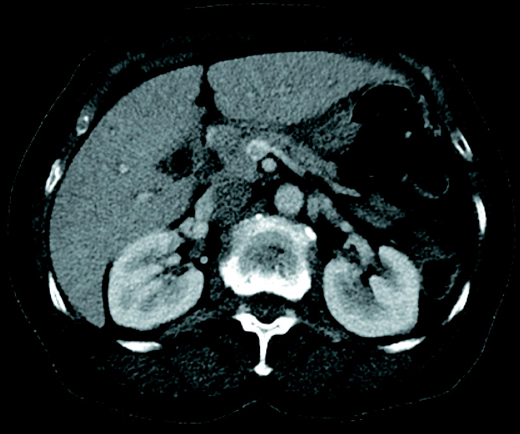
2 The modality provides. 2 The modality provides. Non opacification of main trunk of superior mesenteric vein up to the portosplenic confluence with perivascular fat stranding. Mesenteric vein thrombosis is increasingly recognized as a cause of mesenteric ischemia. 12 Clinically there are two subtypes of mesenteric ischemia.
 Source: researchgate.net
Source: researchgate.net
The symptoms are usually not typical enough to offer a clinical diagnosis. Main portal vein is dilated 145mm. Venous causes of acute mesenteric ischemia are less common 515 of cases 49 and are most often the result of a thrombosis of the superior mesenteric vein SMV. The symptoms are usually not typical enough to offer a clinical diagnosis. Mesenteric vein thrombosis almost always involves the distal small intestine superior mesenteric venous drainage and rarely involves the colon inferior mesenteric venous drainage.
 Source: nejm.org
Source: nejm.org
In patients with extension of thrombosis into the superior mesenteric vein and splenic vein andor presence of hypercoagulability decreased VLS measurements were observed compared with historical control subjects. The symptoms are usually not typical enough to offer a clinical diagnosis. 2 The modality provides. The anatomic site of involvement in acute mesenteric venous thrombosis is most often ileum 64 to 83 percent or jejunum 50 to 81 percent followed by colon. In patients with extension of thrombosis into the superior mesenteric vein and splenic vein andor presence of hypercoagulability decreased VLS measurements were observed compared with historical control subjects.
 Source: radiopaedia.org
Source: radiopaedia.org
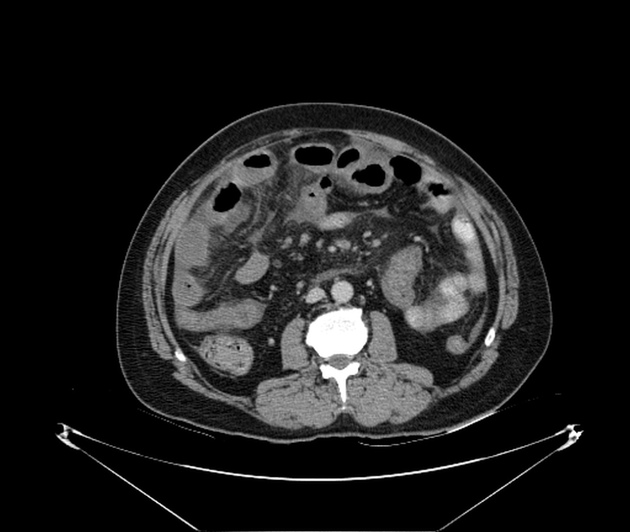
Arrow submucosal varices in biliary enteric anastomosis. Contrast enhanced CT scan of abdomen is quite accurate for diagnosing and differentiating two types of mesenteric venous thrombosis. In one retrospective study on 60 patients with chronic thrombosis of PVs or superior mesenteric veins 39 with variceal bleeding 18 with thrombophilia 9 with variceal bleeding received anticoagulation with recanalization of veins in 3 patients whereas none of the patients who were not anticoagulated recanalized the veins. 1 2 Extension to mesenteric venous arches causes intestinal infarction with a reported mortality of up to 50. 10 Further recurrent bleeding was.
 Source: radiopaedia.org
Source: radiopaedia.org
Chronic mesenteric venous thrombosis accounts for approximately 20 to 40 of total mesenteric venous thrombosis cases and rarely causes intestinal infarction. When you have mesenteric venous thrombosis MVT you have a blood clot in a vein around where your intestines attach to your belly. He had contracted COVID-19 9 days prior. In one retrospective study on 60 patients with chronic thrombosis of PVs or superior mesenteric veins 39 with variceal bleeding 18 with thrombophilia 9 with variceal bleeding received anticoagulation with recanalization of veins in 3 patients whereas none of the patients who were not anticoagulated recanalized the veins. Branching of mesenteric vein 1 2 can be seen in a and c.
 Source: researchgate.net
Source: researchgate.net
Chronic mesenteric ischemia also known as intestinal angina is most often due to arterial atherosclerotic disease. The anatomic site of involvement in acute mesenteric venous thrombosis is most often ileum 64 to 83 percent or jejunum 50 to 81 percent followed by colon. Acute thrombosis commonly presents with abdominal pain and chronic type with features of portal hypertension. MVT may present with acute abdominal pain or may be an asymptomatic incidental finding on abdominal imaging. In one retrospective study on 60 patients with chronic thrombosis of PVs or superior mesenteric veins 39 with variceal bleeding 18 with thrombophilia 9 with variceal bleeding received anticoagulation with recanalization of veins in 3 patients whereas none of the patients who were not anticoagulated recanalized the veins.
 Source: radiopaedia.org
Source: radiopaedia.org
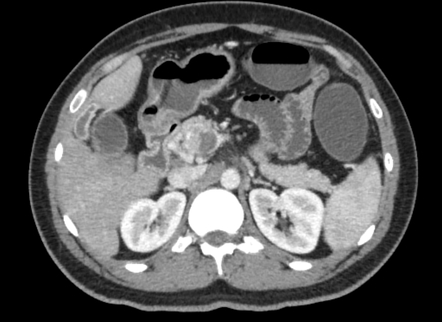
Chronic mesenteric ischemia also known as intestinal angina is most often due to arterial atherosclerotic disease. Gross anatomy Origin and course. In patients with extension of thrombosis into the superior mesenteric vein and splenic vein andor presence of hypercoagulability decreased VLS measurements were observed compared with historical control subjects. Contrast enhanced CT scan of abdomen is quite accurate for diagnosing and differentiating two types of mesenteric venous thrombosis. Spleen is enlarged spanning 20cm.
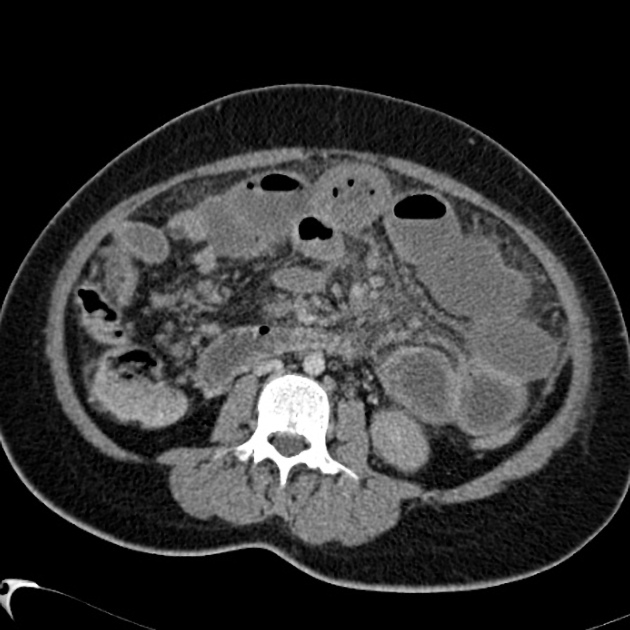 Source: radiopaedia.org
Source: radiopaedia.org
Mesenteric vein thrombosis is increasingly recognized as a cause of mesenteric ischemia. IL intestinal lumen. Non opacification of main trunk of superior mesenteric vein up to the portosplenic confluence with perivascular fat stranding. CT chest abdomen and pelvis revealed an extensive thrombus extending from the portal vein to the superior mesenteric vein. The diagnosis of mesenteric vein thrombosis relies heavily on imaging.
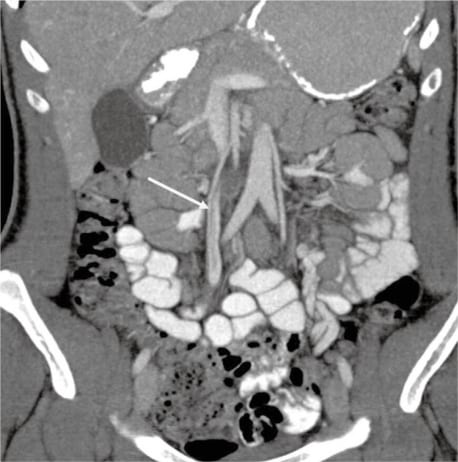 Source: westjem.com
Source: westjem.com
Reversible superior mesenteric vein thrombosis in acute pancreatitis. Arrow submucosal varices in biliary enteric anastomosis. Chronic mesenteric venous thrombosis is differentiated from acute mesenteric venous thrombosis by the existence of collateral venous circulation and cavernoma around the thrombosed vein. Main portal vein is dilated 145mm. Mesenteric vein thrombosis almost always involves the distal small intestine superior mesenteric venous drainage and rarely involves the colon inferior mesenteric venous drainage.
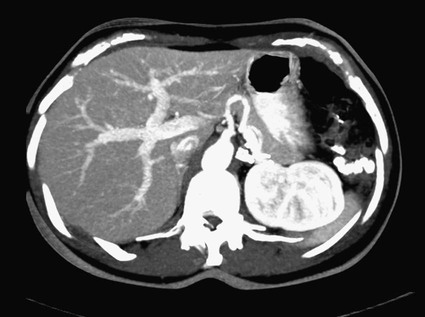 Source: radiologykey.com
Source: radiologykey.com
A 68-year-old man was referred to the general surgeons on account of his abdominal pain of unknown cause. Patients with recovery compared with patients with chronic mesenteric venous thrombosis showed more frequent central lesions p 003. Biphasic CT has become the gold standard in evaluating patients with suspected mesenteric ischemia. Anticoagulation did not influence recovery p 1. Its branches are patent.
 Source: radiopaedia.org
Source: radiopaedia.org
In one retrospective study on 60 patients with chronic thrombosis of PVs or superior mesenteric veins 39 with variceal bleeding 18 with thrombophilia 9 with variceal bleeding received anticoagulation with recanalization of veins in 3 patients whereas none of the patients who were not anticoagulated recanalized the veins. IL intestinal lumen. Mesenteric vein thrombosis almost always involves the distal small intestine superior mesenteric venous drainage and rarely involves the colon inferior mesenteric venous drainage. In one retrospective study on 60 patients with chronic thrombosis of PVs or superior mesenteric veins 39 with variceal bleeding 18 with thrombophilia 9 with variceal bleeding received anticoagulation with recanalization of veins in 3 patients whereas none of the patients who were not anticoagulated recanalized the veins. Patients with recovery compared with patients with chronic mesenteric venous thrombosis showed more frequent central lesions p 003.
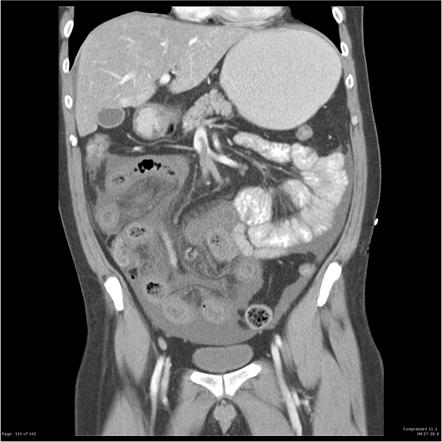 Source: radiopaedia.org
Source: radiopaedia.org
Chronic Portal and Splenic Vein Thrombosis wSinistral Portal HTN A long-standing thrombosis an non-cirrhotic patients is implicated by the presence of a cavernoma venous collateralization features of PH Failure to detect and treat thromboses can result in mesenteric ischemia chronic cavernous transformation. The anatomic site of involvement in acute mesenteric venous thrombosis is most often ileum 64 to 83 percent or jejunum 50 to 81 percent followed by colon. In patients with chronic PVT GI ischemia is frequent. 10 Further recurrent bleeding was. Contrast enhanced CT scan of abdomen is quite accurate for diagnosing and differentiating two types of mesenteric venous thrombosis.
 Source: cureus.com
Source: cureus.com
A Contrast-enhanced maximum intensity projection magnetic resonance MR angiogram reveals collateral vessels from a superior mesenteric vein branch via submucosal varices into liver. VLS enables objective and quantitative determination of GI mucosal ischemia. 1 2 Extension to mesenteric venous arches causes intestinal infarction with a reported mortality of up to 50. 12 Clinically there are two subtypes of mesenteric ischemia. IL intestinal lumen.
 Source: radiologytoday.net
Source: radiologytoday.net
MVT accounts for 1 in 5000 to 15000 inpa - tient admissions and 1 in 1000 emer-. Chronic mesenteric venous thrombosis is differentiated from acute mesenteric venous thrombosis by the existence of collateral venous circulation and cavernoma around the thrombosed vein. 1 2 Extension to mesenteric venous arches causes intestinal infarction with a reported mortality of up to 50. Mesenteric vein thrombosis almost always involves the distal small intestine superior mesenteric venous drainage and rarely involves the colon inferior mesenteric venous drainage. Chronic mesenteric venous thrombosis patients are often asymptomatic with a diagnosis of mesenteric venous thrombosis resulting from incidental findings or portal hypertension.
 Source: radiopaedia.org
Source: radiopaedia.org
A Contrast-enhanced maximum intensity projection magnetic resonance MR angiogram reveals collateral vessels from a superior mesenteric vein branch via submucosal varices into liver. Chronic Portal and Splenic Vein Thrombosis wSinistral Portal HTN A long-standing thrombosis an non-cirrhotic patients is implicated by the presence of a cavernoma venous collateralization features of PH Failure to detect and treat thromboses can result in mesenteric ischemia chronic cavernous transformation. Arrow submucosal varices in biliary enteric anastomosis. Contrast enhanced CT scan of abdomen is quite accurate for diagnosing and differentiating two types of mesenteric venous thrombosis. Chronic mesenteric venous thrombosis accounts for approximately 20 to 40 of total mesenteric venous thrombosis cases and rarely causes intestinal infarction.
This site is an open community for users to submit their favorite wallpapers on the internet, all images or pictures in this website are for personal wallpaper use only, it is stricly prohibited to use this wallpaper for commercial purposes, if you are the author and find this image is shared without your permission, please kindly raise a DMCA report to Us.
If you find this site adventageous, please support us by sharing this posts to your own social media accounts like Facebook, Instagram and so on or you can also bookmark this blog page with the title chronic superior mesenteric vein thrombosis radiology by using Ctrl + D for devices a laptop with a Windows operating system or Command + D for laptops with an Apple operating system. If you use a smartphone, you can also use the drawer menu of the browser you are using. Whether it’s a Windows, Mac, iOS or Android operating system, you will still be able to bookmark this website.






